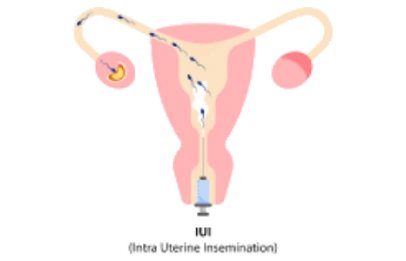
Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI) is a procedure that involves placing sperm inside a woman’s uterus to facilitate fertilization and is a form of assisted conception.
Stages of IUI
- On day 3 of the cycle, the patient usually starts stimulation with medications (either injections or tablets) to induce multiple egg development. The patient is then monitored with ultrasounds until follicular size reaches 20mm in diameter. Then, Insemination is performed after inducing ovulation with HCG (in the form of an injection).
- The husband’s semen is “washed” in the laboratory (called sperm processing or sperm washing). During this process, the sperm is separated from the other components of the semen and concentrated in a much smaller volume. Various media and techniques can be used to perform the washing and separation, depending on the case and preferences of the fertility doctor and laboratory. The sperm processing takes about 20-60 minutes, depending on the technique utilized.
- The patient is prepared; a speculum is placed in the vagina and the cervical area is gently cleaned.
- Then, the separated and washed sperm is placed into the uterine cavity (intrauterine insemination, IUI) using a sterile, thin and soft catheter. Intrauterine insemination has a success rate of 15-25%; it is the most common primary procedure performed in unexplained infertility cases.
- Once IUI is completed, the patient is prescribed Progesterone Supplements.
- Patients do not need to rest after IUI. No restrictions are made on sexual activity or food habits or daily work. A Pregnancy test is then performed after 14 days of IUI. If the patient is pregnant; she is asked to keep taking her medications until 10 weeks gestation.